(par 3. 4.2) Ecosystems & energy-flow

http://www.econguru.com/fundamentals_of_ecology/ecosystems.html Ecosystems An ecosystem extends a community by involving also the abiotic environment, that is, the physical and chemical environment. Energy flow and nutrient cycling(cycling of chemicals) are significant aspects in understand how ecosystems function. An ecosystem often includes cycles and flows that involve dozens of living things as well as non-living matters, not very […]
(par 3. 4.2) Energy Flow in an Ecosystem

http://www.biologydiscussion.com/ecosystem/energy-flow-in-an-ecosystem-with-diagram/6740 Energy has been defined as the capacity to do work. Energy exists in two forms potential and kinetic. Potential energy is the energy at rest {i.e., stored energy) capable of performing work. Kinetic energy is the energy of motion (free energy). It results in work performance at the expense of potential energy. Conversion of […]
(par 3. 4.1) The Food Web
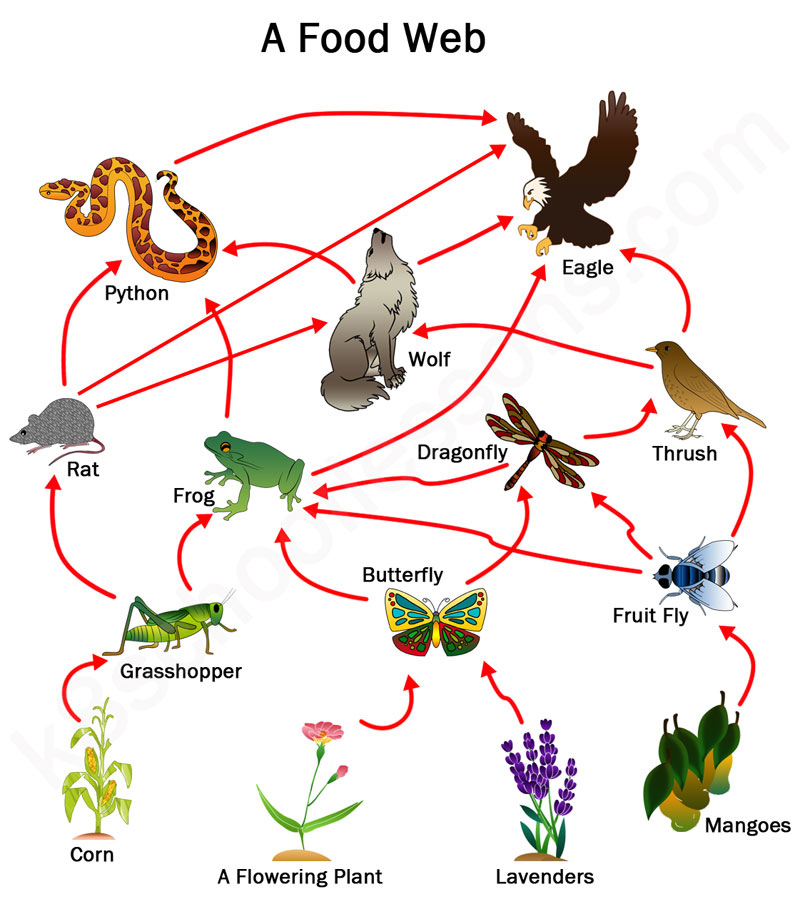
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Food_web From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia A food web (or food cycle) is the natural interconnection offood chains and generally a graphical representation (usually an image) of what-eats-what in an ecological community. Another name forfood web is a consumer-resource system. Ecologists can broadly lump all life forms into one of two categories called trophic levels: 1) theautotrophs, and 2) theheterotrophs. To maintaintheir bodies, grow, […]
