
(par 2.1 ) Ecosystems and habitats
Ecosystems and habitats https://www.le.ac.uk/se/centres/sci/selfstudy/eco2.htm The thin layer of the Earth’s surface where living things are able to survive is called the biosphere. It is about 20km

Ecosystems and habitats https://www.le.ac.uk/se/centres/sci/selfstudy/eco2.htm The thin layer of the Earth’s surface where living things are able to survive is called the biosphere. It is about 20km

The Biotic component and the Abiotic component http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Abiotic_component http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biotic_component From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Biotic components are the living things that shape an ecosystem. A biotic factor is any

ECOLOGY: The study of how living things interact with each other and with their environment A species is a group of organisms that are physically similar

Two Main Components of an Ecosystem by Cara Batema, Demand Media http://everydaylife.globalpost.com/two-main-components-ecosystem-30336.html An ecosystem is a community of living and non-living things, and ecosystems can

http://www.bcb.uwc.ac.za/Sci_Ed/grade10/ecology/abiotic/abiot.htm Abiotic components The way in which plants and animals grow and carry out their different activities is a result of several abiotic factors. These

Elements: Earth, Water, Air, and Fire In This Issue: – Earth, Water, Air, and Fire – Make a Fire Extinguisher Science Project – Traveling Nutrients

The roles of abiotic components in the functioning of the ecosystem http://www.bcb.uwc.ac.za/Sci_Ed/grade10/ecology/abiotic/abiot.htm Abiotic components The way in which plants and animals grow and carry out

What is energy? http://www.eschooltoday.com/energy/kinds-of-energy/all-about-energy.html Look around you. Is anything moving? Can you hear, see or feel anything? Sure… this is because something is making something
Forms of energy http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Forms_of_energy From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Thermal energy is energy of microscopic constituents of matter, which may include both kinetic and potential energy. In the context
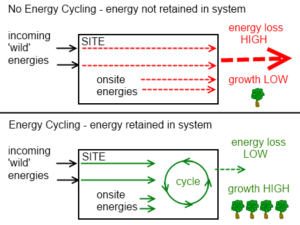
Energy Cycling http://deepgreenpermaculture.com/permaculture/permaculture-design-principles/6-energy-cycling/ The sixth Permaculture Design principle is ‘Energy Cycling’. This design principle is concerned with the recycling of energy by capturing, storing and

Energy Transformation http://environ.andrew.cmu.edu/m3/s3/all_ene_sys.htm The definition of energy as the ability to do work came from the 19th century as steam engines and other work-producing machines
Entropy Explained, With Sheep https://aatishb.github.io/entropy/ (please go to this link to appreciate full explination) From Melting Ice Cubes to a Mystery About Time By Aatish Bhatia Let’s

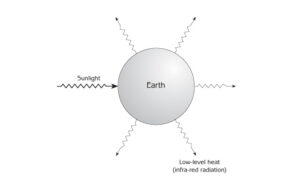
The role of the sun as heat generator on earth and how it contributes to the greenhouse effect. http://www-istp.gsfc.nasa.gov/stargaze/Sun1lite.htm Sunlight and the Earth The Sun

http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Radiation From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or through a material medium.[1][2] This includes electro-magnetic radiation such as radio waves, visible

http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Photoperiodism From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Photoperiodism is the physiological reaction of organisms to the length of day or night. It occurs in plants and animals. Photoperiodism can also

Introduction to photosynthesis http://www.eschooltoday.com/photosynthesis/introduction-to-photosynthesis.html Every living creature needs food or energy to survive. Some depend on others for food and energy, whiles others can produce
The Laws of Thermodynamics and how it applies to the transfer of energy through the ecosystem. http://www.gerrymarten.com/human-ecology/chapter08.html The Laws of Thermodynamics We all depend upon

Thermodynamic Laws & ecosystems The Laws of Thermodynamics and how it applies to the transfer of energy through the ecosystem. http://www.gerrymarten.com/human-ecology/chapter08.html The Laws of Thermodynamics

Where Do the Laws of Nature Come From Where Do the Laws of Nature Come From? http://www.scienceandreligiontoday.com/2010/04/15/where-do-the-laws-of-nature-come-from/ From Robert Lawrence Kuhn, host and creator of Closer To

Where Do the Laws of Nature Come From? http://www.scienceandreligiontoday.com/2010/04/15/where-do-the-laws-of-nature-come-from/ From Robert Lawrence Kuhn, host and creator of Closer To Truth: I live my life, plan and do,

https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Water_distribution_on_Earth From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia A graphical distribution of the locations of water on Earth Visualisation of the distribution (by volume) of water on

Atmosphere http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Atmosphere From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia This article is about atmospheres in general. For Earth’s atmosphere, see Atmosphere of Earth. An atmosphere (New Latin atmosphaera, created in the

Chapter 1. Introduction Chapter 2. Organic matter decomposition and the soil food web Chapter 3. Natural factors influencing the amount of organic matter Chapter 5.

http://www.vaderstad.com/en/knowhow/soil-basic The building blocks of soil The soil that is cultivated to create a seedbed only consists to half of solid material, while the remainder

http://www.eschooltoday.com/rocks/what-is-a-rock.html They are very tiny grains of different minerals, compressed together in chemical reaction to form a bigger mass. Rocks make up non-water part of

This topic has four questions: What is organic matter? What are the 4 main steps in degradation of organic matter? What is the impact of

http://www.earthwormsoc.org.uk/earthworm-information/earthworm-information-page-3 Soil structure Earthworms have been called ‘ecosystem engineers’. Much like human engineers, earthworms change the structure of their environments. Different types of earthworms can

How to identify your soil types https://www.dammannsgardenco.com/blog/how-to-identify-soil-types Recently, we’ve noticed more and more people are interested in growing their own food. Since growing yummy vegetables

http://broome.soil.ncsu.edu/ssc012/Lecture/topic8.htm Physical Properties Features of the soil profile and the soil horizons are often described in the field in terms of the soil’s physical properties.

http://nerrs.noaa.gov/doc/siteprofile/acebasin/html/envicond/soil/slform.htm A number of conceptual models of soil formation have been postulated over the years. The two that have been key in our basic understanding

Soil Formation & Soil Horizons http://nerrs.noaa.gov/doc/siteprofile/acebasin/html/envicond/soil/slform.htm A number of conceptual models of soil formation have been postulated over the years. The two that have been

CLIMATE: What Effect Does Geography Have on Climate? http://science.opposingviews.com/effect-geography-climate-5100.html by John Peterson, Demand Media Geography and climate are interrelated. Ablestock.com/AbleStock.com/Getty Images Geography has a primary

Landforms http://www.edu.pe.ca/southernkings/glacierjf.htm Landforms are natural features of the landscape, natural physical features of the earth’s surface, for example, valleys, plateaus, mountains, plains, hills, loess, or

What Effect Does Geography Have on Climate? http://science.opposingviews.com/effect-geography-climate-5100.html by John Peterson, Demand Media Geography and climate are interrelated. Ablestock.com/AbleStock.com/Getty Images Geography has a primary effect

Environmental Effects USDA Forest Service Southern Region, February 1989; Technical Publication R8-TP 11 Prescribed burning has direct and indirect effects on the environment. Proper use

Salinity http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Main_Page From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Salinity is the saltiness or dissolved salt content of a body of water (see also soil salinity). Salinity is an important factor in determining

Salinity and water quality fact sheet http://www.environment.gov.au/water/quality/publications/factsheet-salinity-and-water-quality Department of Sustainability, Environment, Water, Population and Communities, 2012 Salinity and water quality fact sheet (PDF – 888

Nutrients http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Main_Page From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Nutrients are the components in foods that an organism utilizes to survive and grow. Macronutrients provide the bulk energy

What are Nutrients? https://byjus.com/biology/nutrients/ “Nutrients are the compounds in food that provide us with energy that facilitates repair and growth and helps to carry out

“If a tree dies, plant another in its place.” – Carl Linnaeus For all forms of life, plants form the basic food staples, and this

http://cnvc-cnvc.ca/view_article.cfm?id=181 Vegetation is a key component of an ecosystem and, as such, is involved in the regulation of various biogeochemical cycles, e.g., water, carbon, nitrogen.

MG Manual Reference 4, Ch. 1, pp. 25 – 29 https://ag.arizona.edu/pubs/garden/mg/botany/physiology.html The three major plant functions that are the basics for plant growth and development are photosynthesis, respiration,

http://www.mbgnet.net/bioplants/adapt.html Plants have adaptations to help them survive (live and grow) in different areas. Adaptations are special features that allow a plant or animal to

http://www.summitpost.org/heterotrophic-plants/591392 Plants generally make their own food through the process of photosynthesis. These plants are called autotrophs (self-feeding). However, some species have taken a different

http://www.tutorvista.com/science/forest-ecosystem-animals Introdction to forest ecosystem animals : In the Forest ecosystem animals are the consumers.They influence the flow of energy and cycling of nutrients through

http://www.onegreenplanet.org/animalsandnature/animals-that-help-us-to-survive/ Jenna Bardroff, September 5, 2014 The earth, its ecosystems, and its creatures are all deeply connected. Thus, the existence of many species depends on the survival of

http://www.rainforestconservation.org/rainforest-primer/2-biodiversity/f-animals/1-roles-of-animals-in-tropical-rainforests/ Pollination: Many animals are essential in the reproductive processes of forest plants. Bats are known to be pollinators of more than 300 plant species

http://science.jrank.org/pages/1967/Decomposition.html Decomposition is the natural process by which large organic materials and molecules are broken down into simpler ones. The ultimate products of decomposition are
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Decomposition From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia A mummified rat. Blowfly and fly larvae on 5-day old corpse of South African Porcupine (Hystrixafricaeaustralis) Stages of death Pallor mortis

http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Plant_litter From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Leaf litter, mainly White Beech, Gmelinaleichhardtii, from Black Bulga State Conservation Area, NSW, Australia Litterfall, plant litter, leaf litter, tree litter, soil litter, or duff, is

http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anthropocene From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia The Anthropocene is an informal geologic chronological term for the proposed epoch that began when human activities had a significant global impact on the Earth‘s ecosystems.[1] The term—which

http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human%E2%80%93wildlife_conflict From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Grand Canyon National Park hosts millions of visitors every year and is home to a population of Rocky Mountain elk. Interactions

http://www.globalchange.umich.edu/globalchange1/current/lectures/kling/ecosystem/ecosystem.html “I bequeathe myself to the dirt, to grow from the grass I love; If you want me again, look for me under your boot-soles.”

http://www.theguardian.com/environment/georgemonbiot/2014/dec/12/how-whale-poo-is-connected-to-climate-and-our-lives Friday 12 December 2014 07.00 GMT George Monbiot Not only does nutrient-rich whale poo help reverse the effects of climate change – it’s a