(par 3. 5 ) Biomass and the availability of energy
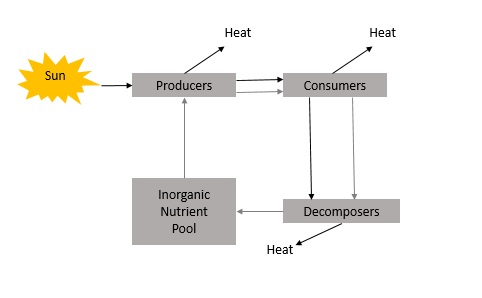
Biomass & availability of energy http://www.marietta.edu/~biol/102/ecosystem.html Overview The main concepts we are trying to get across in this section concern how energy moves through an ecosystem. If you can understand this, you are in good shape, because then you have an idea of how ecosystems are balanced, how they may be affected by human activities, […]
(par 3. 5 ) Ecosystems & energy-flow

Ecosystems & Energy-flow http://www.econguru.com/fundamentals_of_ecology/ecosystems.html Ecosystems An ecosystem extends a community by involving also the abiotic environment, that is, the physical and chemical environment. Energy flow and nutrient cycling(cycling of chemicals) are significant aspects in understand how ecosystems function. An ecosystem often includes cycles and flows that involve dozens of living things as well as non-living […]
(par 3. 5.2) Secondary Production

Secondary production Secondary production is the generation of biomass of heterotrophic (consumer) organisms in a system. This is driven by the transfer of organic material between trophic levels, and represents the quantity of new tissue created through the use of assimilated food. Secondary production is sometimes defined to only include consumption of primary producers by herbivorous consumers[2] (with tertiary production referring to carnivorous consumers),[3] but is more commonly […]
