(par 1.3.2) Open System (taken from Wikipedia)
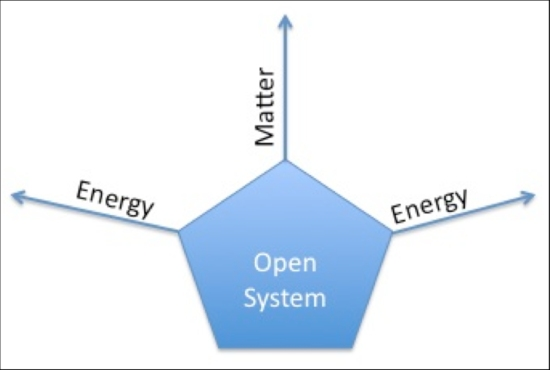
Open system http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Main_Page From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Open system have input and output flows, representing exchanges of matter, energy or information with its surroundings. A opened system is a system that has external interactions. Such interactions can take the form of information, energy, or material transfers into or out of the system boundary, depending on the discipline which […]
(par 1.3.2) Isolated System (taken from Wkipedia)

Isolated system http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Main_Page From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia In physical science, an isolated system is either (1) a thermodynamic system which is completely enclosed by walls through which can pass neither matter nor energy, though they can move around inside it; or (2) a physical system so far removed from others that it does not interact with them, though it is subject […]
(par 1.3.2) Closed Ecological System (taken from Wikipedia)

Closed ecological system http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Main_Page From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Closed ecological systems (CES) are ecosystems that do not rely on matter exchange with any part outside the system. The term is most often used to describe small manmade ecosystems. Such systems are scientifically interesting and can potentially serve as a life support system during space flights, in space stations or space habitats.[1] In a closed ecological […]
