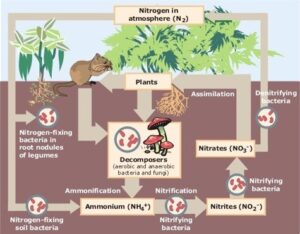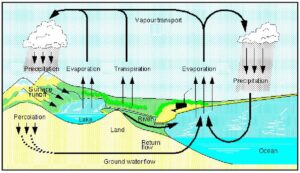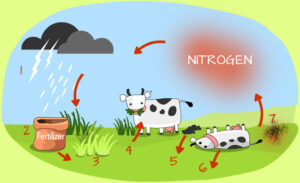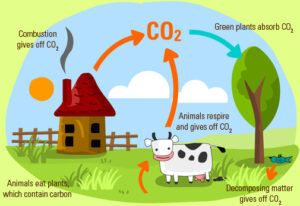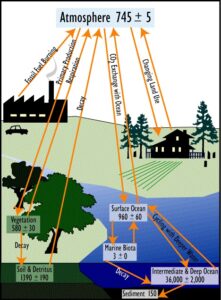
(par 3. 3 ) A graphic depiction of the Biogeochemical Cycles
http://homepages.nyu.edu/~pet205/biogeochem1.html BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES Biogeochemical Cycle : the cycling of chemical elements required by life between the living and nonliving parts of the environment. Some examples